New Innovations in Artificial Vision Systems in the Infrared Enabled by CMOS Si Sensors
Dr. Abhijit Biswas
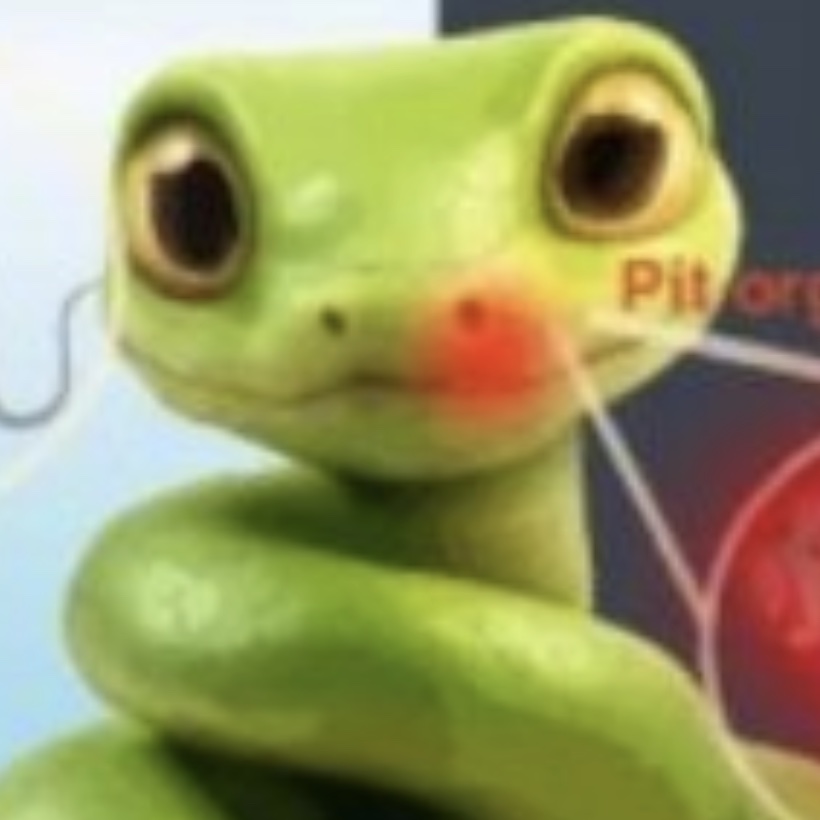



In a “hybrid route” combining evaporation and blade-coating to deposit perovskite solar cells on silicon bottom cells, they produced tandem solar cells with efficiencies approaching 28 percent. (read for more)
As 2025 draws to a close, we want to thank our customers, partners and colleagues for another busy, productive year. Together, we’ve continued to push what’s possible in vacuum, gas, plasma and surface analysis – from new accessories and application developments to a strong presence at key conferences around the world. (read for more)
Passau, January 19, 2026 – For more than 50 years, quality, reliability, and continuous improvement have been at the core of Thyracont Vacuum Instruments GmbH. As formal confirmation of these long-established quality standards, the company decided on certification in accordance with the international quality management standard ISO 9001. At the same time, the certification provides a solid foundation for further growth and the development of new business partnerships.
Longmont, CO—January 20, 2026. The new VaporTech® Signature PVD Finishes Collection™ includes four new PVD finishes designed to enhance consumer products with superior durability, refined aesthetics, and a luxurious appearance. The collection includes four elevated PVD colors: midnight black, autumn bronze, stormy gray, and sunset gold.







Since 2000 Vacuum Technology & Coating Magazine has been the industry's leading source for the latest articles, news, and product and service information. Below we describe some of the terms that you will find in a typical issue of VT&C.
Vacuum Coating (Vacuum Deposition and Thin Film Deposition) is the process of depositing a film or other material atom by atom or molecule by molecule onto a surface in a low pressure environment or vacuum.
Physical Vapor Deposition or PVD refers to vacuum deposition methods which involve the material (which is being deposited) going from a condensed phase to a vapor phase and then to a thin film condensed phase. Sputtering and evaporation are common PVD processes.
Sputtering refers to a type of process used to deposit thin films and employs a plasma to bombard and eject atoms from a target source.
Evaporation refers to the heated source material being evaporated in a vacuum. Vacuum allows vapor particles to travel directly to the target object, where they condense back to a solid state. (called a Deposition Source) refers to a type of process used to deposit thin films and employs a plasma to bombard and eject atoms from the target source (called a Deposition Source).
Vacuum Hardware refers to the types of hardware and components that are used in the vacuum process. There are many types of hardware used in this process, some examples are flanges, fittings, seals, valves, and chambers.
Thin Film Metrology involves determining the optimal thickness, composition and/or condition of a coating through various techniques and mathematical calculations.
Gas Analytical Systems are used in the analysis of residual gases within a low pressure environment or vacuum.
Vacuum Pumps are devices that remove gas atoms and molecules for the purpose of leaving behind a partial vacuum. Some examples of types of vacuum pumps are rotary vane pumps, diaphragm pumps, and scroll pumps.
Every issue of VT&C includes a product showcase focused on a specific topic relevant to Vacuum Processing, please see our 2026 editorial calendar which lists the topic for each issue.